
How to Avoid Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. This issue is particularly prevalent among older people, due to factors such as reduced mobility, underlying health conditions and prolonged periods of inactivity.
However, there are many strategies that can help prevent DVT. Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding and avoiding this potentially life-threatening condition.
Understanding DVT
Symptoms of DVT can include swelling, pain, redness and warmth in the affected leg. If left untreated, DVT can lead to serious complications, such as Pulmonary Embolism, which occurs when a clot travels to the lungs and blocks blood flow.
Older people are at a higher risk due to factors such as:
Age-related changes in blood flow and vessel elasticity
Coexisting conditions (e.g. heart disease and obesity)
Medications that affect blood clotting
Reduced mobility from illness or injury
Preventive Measures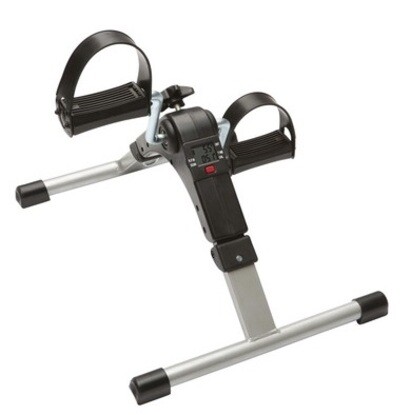 
1. Stay Active and avoid long periods of inactivity
If you spend a lot of time sitting or lying down, movement breaks are really important. It’s vital to take breaks every hour to stand up, stretch and walk around.
Regular physical activity like walking, swimming or gentle stretching can improve circulation and reduce the risk of DVT.
As well as movement breaks, light activity can help a lot, even just moving feet or legs while seated. Exercising with a Pedal Exerciser is one of the best ways to stay fit and help reduce the risk of DVT.
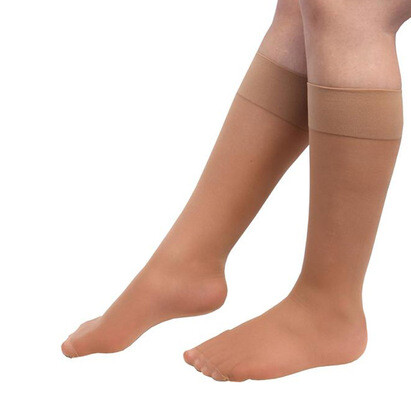
2. Wear Compression Hosiery
Compression hosiery helps maintain proper blood flow and reduce swelling. They are particularly beneficial during long journeys or if you are bedridden. Graduated compression socks and support tights are comfortable and effective options.
3. Maintain Hydration
Staying well-hydrated helps maintain normal blood consistency and flow. Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially if you are on medications that may lead to dehydration.
4. Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins can help maintain a healthy weight and improve vascular health. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids (like fish and flaxseeds) can have blood-thinning effects that may help prevent clots.
5. Manage Underlying Conditions
Chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension and heart disease can increase the risk of DVT. Regular medical check-ups and appropriate management of these conditions are really important. Follow medical advice on managing medications, especially those that affect blood coagulation.
6. Seek Medical Attention Post-Surgery or Illness
After surgery or a spell in hospital, especially following orthopaedic or pelvic surgery, patients should discuss DVT prevention strategies with their healthcare providers. This may include medication or specific physical activity plans during recovery.
7. Be Mindful of Medications
Some medications can increase the risk of DVT. Ensure that the elderly person is aware of these risks and talks with their doctor about any concerns regarding their medication regimen.
In conclusion, preventing DVT is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. By implementing proactive measures, such as staying active, using compression hosiery and managing underlying health conditions, the risks associated with DVT can be significantly reduced.
Regular communication with healthcare professionals and awareness of symptoms is also vital for timely intervention. An informed and proactive approach can lead to healthier aging and a lower incidence of this serious condition.
